Tropical ecosystem meals chains, the colourful and complex tapestries of lifestyles, get to the bottom of sooner than our eyes, inviting us to discover the attention-grabbing relationships that maintain those lush ecosystems.
Inside of those verdant nation-states, vegetation, the principle manufacturers, harness daylight to create the basis of the meals chain. Herbivores, the principle customers, graze upon this plant lifestyles, whilst carnivores, the secondary customers, banquet upon the herbivores. On the apex of this hierarchy, best predators reign because the tertiary customers.
Definition and Evaluation of Tropical Ecosystem Meals Chain
A meals chain is a linear series of organisms during which vitamins and effort move, beginning with a manufacturer organism and finishing with a best predator. In tropical ecosystems, meals chains are specifically complicated and numerous because of the abundance of species and the nice and cozy, humid local weather.A
standard tropical ecosystem meals chain starts with number one manufacturers, akin to vegetation and algae, which convert daylight into power thru photosynthesis. Those manufacturers are then fed on via number one customers, akin to herbivores and small omnivores. Secondary customers, akin to carnivores and bigger omnivores, then devour the principle customers.
Tertiary customers, akin to best predators, are on the absolute best degree of the meals chain and devour the secondary customers.
Manufacturers and Number one Shoppers

Tropical ecosystems are teeming with lifestyles, and on the basis of this colourful internet lies the meals chain. Number one manufacturers, akin to vegetation, shape the cornerstone of this chain, whilst number one customers, basically herbivores, play a an important position in changing plant topic into animal biomass.
Number one Manufacturers: Vegetation
- Tropical ecosystems are house to a various array of vegetation, starting from towering bushes to sprawling shrubs and luxurious undergrowth. Those vegetation are the principle manufacturers, using daylight, water, and carbon dioxide to create their very own meals thru photosynthesis.
- Vegetation give you the basis for all of the meals chain, changing inorganic topic into natural compounds that can be used via different organisms.
Number one Shoppers: Herbivores, Tropical ecosystem meals chain
- Number one customers, predominantly herbivores, feed immediately on plant topic. Those animals have developed quite a lot of diversifications to successfully devour and digest plant subject material.
- Herbivores possess specialised digestive techniques, together with longer digestive tracts and specialised enzymes, enabling them to damage down tricky plant fibers and extract vitamins.
- Examples of number one customers in tropical ecosystems come with bugs, rodents, birds, and bigger herbivores like elephants and giraffes.
Secondary and Tertiary Shoppers: Tropical Ecosystem Meals Chain

Secondary customers, repeatedly referred to as carnivores, occupy the center tier of the meals chain, feeding totally on herbivores and different smaller carnivores. They play a an important position in regulating herbivore populations, fighting them from overgrazing crops and keeping up the steadiness of the ecosystem.
Diversifications akin to sharp tooth and claws, enhanced senses, and larger agility let them successfully seize and devour their prey.
Tertiary Shoppers
On the apex of the meals chain live tertiary customers, sometimes called best predators. Those ambitious carnivores feed solely on different carnivores, exerting a profound affect on all of the ecosystem. Their diversifications, akin to tough jaws, specialised looking methods, and prepared sensory belief, permit them to dominate the meals chain and keep watch over the populations in their prey.
Tertiary customers play a very important position in keeping up biodiversity and fighting any unmarried species from changing into too dominant.
Decomposers and Nutrient Biking
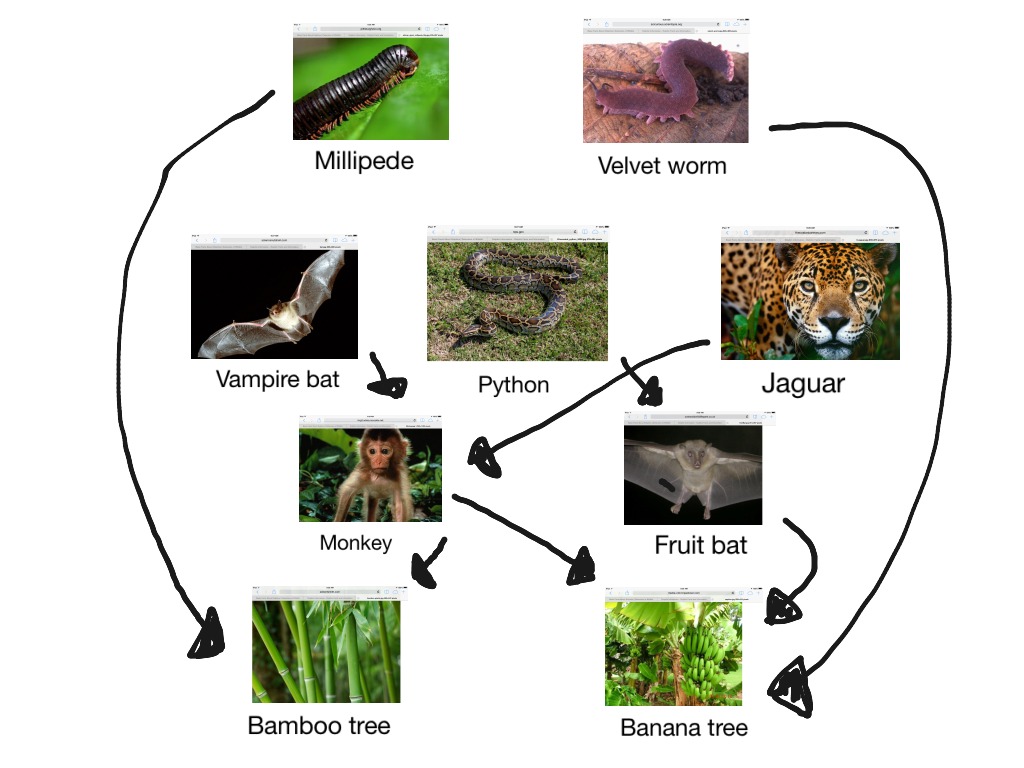
Decomposers play a very important position within the tropical ecosystem meals chain via breaking down useless vegetation and animals, returning vitamins to the soil and making them to be had for different organisms.
Nutrient biking is the method wherein vitamins are transferred from the surroundings to organisms and again to the surroundings. This procedure is very important for keeping up ecosystem steadiness and making sure the supply of vitamins for plant enlargement.
Decomposers
- Decomposers are organisms, akin to micro organism, fungi, and worms, that destroy down useless natural topic.
- They free up vitamins again into the soil, which can be utilized via vegetation and different organisms.
- Decomposers assist to recycle vitamins and deal with the steadiness of the ecosystem.
Nutrient Biking
- Nutrient biking comes to the switch of vitamins from the surroundings to organisms and again to the surroundings.
- Vitamins are crucial for plant enlargement and different ecosystem processes.
- Nutrient biking is helping to deal with the steadiness of the ecosystem and make sure the supply of vitamins for plant enlargement.
Power Go with the flow and Trophic Ranges
Power flows thru a tropical ecosystem meals chain in a unidirectional approach, from manufacturers to customers and in the long run to decomposers. Every trophic degree represents a step on this power switch procedure.
Ecological Pyramids
Ecological pyramids are graphical representations that illustrate the distribution of power or biomass at other trophic ranges. They assist visualize the relative abundance and effort content material at every degree. There are 3 major forms of ecological pyramids:
-
-*Pyramid of Numbers
Depicts the collection of organisms at every trophic degree.
-*Pyramid of Biomass
Represents the entire mass of organisms at every trophic degree.
-*Pyramid of Power
Displays the quantity of power to be had at every trophic degree.
Those pyramids in most cases have a vast base representing manufacturers, adopted via narrower ranges for number one, secondary, and tertiary customers. The form of the pyramid displays the power loss that happens because it strikes up the meals chain.
Meals Webs and Interconnections
The meals webs in tropical ecosystems are intricate networks of interconnected relationships amongst organisms. Those ecosystems space an infinite range of species, leading to complicated interactions and dependencies.
Inside of those meals webs, quite a lot of symbiotic relationships play necessary roles in keeping up the ecosystem’s steadiness. Mutualism, the place each species have the benefit of the affiliation, is commonplace. For instance, ants and acacia bushes shape a mutualistic courting the place ants give protection to the tree from herbivores in alternate for the sugary nectar produced via the tree.
Commensalism
Commensalism, the place one species advantages whilst the opposite is neither harmed nor benefited, may be seen. For example, epiphytic vegetation that develop on tree branches make the most of the tree’s enhance with out affecting the tree’s enlargement.
Parasitism
Parasitism, the place one species advantages on the expense of some other, is some other prevalent symbiotic courting. Parasitic vegetation, akin to mistletoe, connect themselves to host bushes and derive vitamins from them, probably weakening the host.
Human Affects and Conservation
Human actions can considerably disrupt the subtle steadiness of tropical ecosystems and their meals chains. It’s important to spot and deal with those affects to keep the integrity and biodiversity of those necessary ecosystems.
Conservation measures and methods are crucial to give protection to and keep tropical ecosystems. By means of working out the human affects and enforcing efficient conservation practices, we will be able to make sure that the long-term well being and sustainability of those precious ecosystems.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
- Deforestation, urbanization, and infrastructure building result in habitat loss and fragmentation, decreasing the to be had assets for species and disrupting their interactions inside the meals chain.
- Habitat loss may end up in inhabitants declines, species extinctions, and alterations in network construction.
Overexploitation
- Unsustainable harvesting of assets, akin to looking and fishing, can fritter away populations of key species, disrupting the meals chain and ecosystem steadiness.
- Overexploitation can result in species declines, trophic cascades, and ecosystem degradation.
Invasive Species
- Creation of non-native species can disrupt the equilibrium of tropical ecosystems.
- Invasive species would possibly compete with local species for assets, transmit illnesses, or regulate meals webs, resulting in biodiversity loss and ecosystem disruption.
Air pollution
- Air pollution from business, agricultural, and home assets can input tropical ecosystems, harming species and disrupting the meals chain.
- Air pollution can gather in organisms, inflicting well being issues, reproductive impairments, and alterations in ecosystem functioning.
Conservation Measures and Methods
To give protection to and keep tropical ecosystems, quite a lot of conservation measures and methods may also be applied, together with:
- Organising secure spaces, akin to nationwide parks and flora and fauna reserves, to safeguard important habitats and species.
- Selling sustainable land-use practices, akin to agroforestry and community-based conservation, to attenuate habitat loss and fragmentation.
- Enforcing sustainable harvesting practices and regulating overexploitation to verify the long-term viability of species populations.
- Controlling the advent and unfold of invasive species thru quarantine measures and habitat control.
- Decreasing air pollution assets and enforcing waste control methods to give protection to ecosystems from damaging contaminants.
- Attractive native communities and indigenous peoples in conservation efforts to foster stewardship and sustainable useful resource control.
Most sensible FAQs
What’s a meals chain?
A meals chain is a linear series of organisms during which vitamins and effort move, beginning with manufacturers and finishing with best predators.
What’s the position of decomposers in a meals chain?
Decomposers destroy down useless organisms and waste merchandise, freeing vitamins again into the ecosystem.
How does human task affect tropical ecosystem meals chains?
Human actions akin to deforestation, air pollution, and local weather exchange can disrupt meals chains via changing habitats, decreasing biodiversity, and disrupting power float.

