The rainforest meals chain, a intricate tapestry of existence, unravels ahead of our eyes, inviting us to discover the bizarre interdependence of organisms inside this colourful ecosystem.
From towering timber that extend for the heavens to the smallest microorganisms hidden within the soil, every participant within the rainforest meals chain performs a a very powerful function in keeping up the sophisticated stability of this herbal marvel.
Ecosystem Construction and Interactions

Rainforests are characterised by means of a fancy internet of interactions between vegetation, animals, and microorganisms. Those interactions are very important for keeping up the ecosystem’s stability and making sure the survival of its various species.
Crops, as number one manufacturers, shape the basis of the rainforest ecosystem. They convert daylight into power thru photosynthesis, offering meals for herbivores and omnivores. Herbivores, akin to bugs, birds, and mammals, devour vegetation and play a a very powerful function in controlling plant populations and combating overgrowth.
Keystone Species
Keystone species are organisms that experience a disproportionately massive have an effect on on their ecosystem relative to their abundance. In rainforests, keystone species come with most sensible predators like jaguars and eagles. Those predators control populations of herbivores, combating them from overgrazing and permitting plant populations to thrive.
Keystone species additionally affect the distribution and behaviour of different species, growing cascading results during the ecosystem.
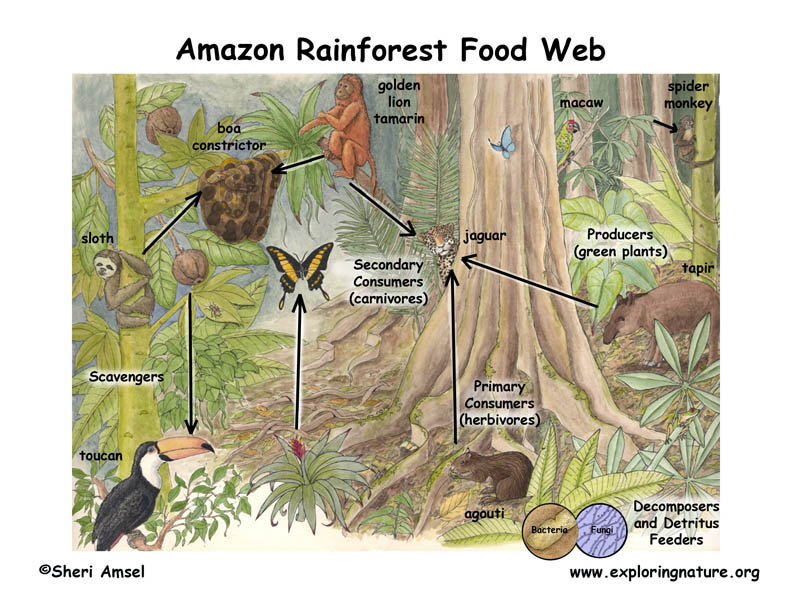
Manufacturers and Shoppers
The rainforest is a colourful ecosystem teeming with existence, the place the complicated interaction between manufacturers and customers bureaucracy the basis of the meals chain.
Number one Manufacturers
The main manufacturers of the rainforest are the autotrophic organisms that convert daylight into power thru photosynthesis. Those come with:
- Bushes:Towering giants that shape the cover and fortify an unlimited array of existence.
- Shrubs:Smaller woody vegetation that supply refuge and meals for quite a lot of animals.
- Vines:Hiking vegetation that extend for the daylight, growing dense plants and habitat.
Shoppers
Shoppers depend at the manufacturers for sustenance and may also be categorized into quite a lot of ranges in line with their feeding conduct:
- Herbivores:Number one customers that feed on vegetation, akin to deer, tapirs, and monkeys.
- Carnivores:Secondary customers that feed on herbivores, akin to jaguars, ocelots, and snakes.
- Omnivores:Feed on each vegetation and animals, akin to bears, raccoons, and birds.
- Best Predators:Apex predators that haven’t any herbal predators, akin to jaguars and harpy eagles.
Nutrient Biking and Decomposition
Nutrient biking is the method through which vitamins are transferred inside an ecosystem. It comes to the breakdown of natural subject, the discharge of vitamins into the soil, and the uptake of those vitamins by means of vegetation. Decomposition is the method through which natural subject is damaged down into more practical compounds by means of decomposers akin to fungi and micro organism.
Nutrient biking is very important for the functioning of an ecosystem. It guarantees that vitamins are to be had to vegetation, that are the main manufacturers within the ecosystem. With out nutrient biking, vegetation would now not be capable to develop and the ecosystem would cave in.
Decomposers
Decomposers are organisms that spoil down natural subject into more practical compounds. They play an important function in nutrient biking by means of liberating vitamins again into the soil. Decomposers come with fungi, micro organism, and different organisms that are living within the soil.
- Fungi are the main decomposers of picket and different plant subject material.
- Micro organism are chargeable for decomposing all kinds of natural subject, together with animal carcasses and plant clutter.
Diversifications and Symbiotic Relationships
Rainforest organisms have advanced distinctive diversifications to thrive of their difficult atmosphere. Those diversifications vary from bodily characteristics to behavioral methods. Moreover, symbiotic relationships between species play a a very powerful function in keeping up the rainforest ecosystem’s stability and steadiness.
Diversifications for Survival
-
-*Camouflage
Many rainforest animals, akin to frogs, snakes, and bugs, have advanced camouflage to mix in with their setting, protective them from predators.
-*Cryptic Colour
Positive species, like stick bugs and leaf beetles, have cryptic colour, making them tricky to tell apart from their setting, offering a bonus in predator avoidance.
-*Nocturnal Habits
Many rainforest animals are nocturnal, keeping off predators lively all the way through the day and exploiting the lowered festival for meals and assets at evening.
Symbiotic Relationships
Symbiotic relationships are mutually advisable interactions between other species. Those relationships play a vital function in rainforest ecosystems.
Mutualism
-
-*Pollination
Bees and different bugs pollinate rainforest vegetation, making sure their copy and genetic variety. In go back, the vegetation give you the pollinators with nectar and pollen as meals.
-*Seed Dispersal
Birds and mammals disperse rainforest plant seeds, assisting in plant copy and colonization of recent spaces. The animals get pleasure from eating the fruit or seed pulp.
Commensalism
-
-*Epiphytes
Epiphytes, akin to orchids and ferns, develop on timber, the usage of them as fortify. They don’t hurt the timber and get pleasure from get right of entry to to daylight and moisture.
-*Hitchhiking
Some bugs and small animals hitchhike on greater animals, gaining coverage and transportation with out harming the host.
Threats to the Rainforest Meals Chain

The stableness of the rainforest meals chain is below danger from numerous human actions. Those come with:
- Deforestation: The clearing of rainforest for logging, agriculture, and different functions destroys the habitat of many species, disrupting the meals chain.
- Air pollution: Insecticides, fertilizers, and different pollution can acquire within the rainforest ecosystem, harming vegetation and animals.
- Local weather trade: Emerging temperatures and adjustments in precipitation patterns can modify the distribution and abundance of species, disrupting the meals chain.
The effects of those threats may also be critical. Deforestation can result in the extinction of species, whilst air pollution may cause well being issues in each vegetation and animals. Local weather trade can disrupt all of the meals chain, resulting in a decline in biodiversity and ecosystem services and products.
Conservation and Control
Holding the intricate tapestry of rainforest ecosystems is a very powerful for the planet’s well being. Conservation and control methods are very important to safeguard those biodiversity hotspots and make sure their ecological integrity.
Protective Keystone Species, Rainforest meals chain
Keystone species, akin to most sensible predators and pollinators, play disproportionately influential roles in keeping up ecosystem stability. Protective those species is necessary as their decline could have cascading results during the meals chain.
Keeping up Habitat Connectivity
Habitat fragmentation, brought about by means of human actions akin to deforestation, disrupts species’ motion and gene drift. Keeping up habitat connectivity thru corridors and secure spaces lets in animals to get right of entry to meals, associates, and refuge, making sure genetic variety and resilience.
FAQ Useful resource
What’s the number one supply of power within the rainforest meals chain?
The solar is the main supply of power, which vegetation seize thru photosynthesis and convert into chemical power.
What are some examples of keystone species within the rainforest?
Keystone species within the rainforest come with fig timber, which give meals for quite a lot of animals, and military ants, which assist regulate populations of different bugs.
What are the most important threats to the rainforest meals chain?
Deforestation, air pollution, and local weather trade are primary threats to the rainforest meals chain, as they disrupt the sophisticated stability of the ecosystem.

