The grasslands meals chain, a colourful tapestry of lifestyles, unfolds within the huge expanses of the sector’s temperate and tropical areas. It is a dynamic device the place manufacturers, customers, and decomposers play intricate roles in keeping up the subtle steadiness of this distinctive ecosystem.
From the towering grasses that sway within the wind to the varied array of animals that decision the grasslands house, each and every species contributes to the intricate internet of interactions that outline this attention-grabbing ecosystem.
Grasslands Ecosystem Assessment

Grasslands are huge, open ecosystems ruled through grasses and different herbaceous crops. They’re characterised through a temperate local weather with average rainfall, sizzling summers, and chilly winters. The soil in grasslands is most often deep and fertile, with a top natural subject content material.Grasslands
are discovered on all continents with the exception of Antarctica, and so they quilt roughly 25% of the Earth’s land floor. One of the crucial most famed grasslands come with the Nice Plains of North The usa, the Pampas of South The usa, the steppes of Eurasia, and the savannas of Africa.
Sorts of Grasslands
There are lots of various kinds of grasslands, each and every with its personal distinctive traits. One of the crucial maximum not unusual sorts come with:
- Temperate grasslandsare present in areas with a average local weather and average rainfall. They’re characterised through tall, dense grasses and quite a lot of wildflowers.
- Tropical grasslandsare present in areas with a heat local weather and top rainfall. They’re characterised through tall, coarse grasses and quite a lot of timber and shrubs.
- Subtropical grasslandsare present in areas with a heat local weather and average rainfall. They’re characterised through a mixture of tall and quick grasses, in addition to quite a lot of timber and shrubs.
- Mediterranean grasslandsare present in areas with a Mediterranean local weather. They’re characterised through quick, sparse grasses and quite a lot of wildflowers.
Manufacturers within the Grasslands Meals Chain
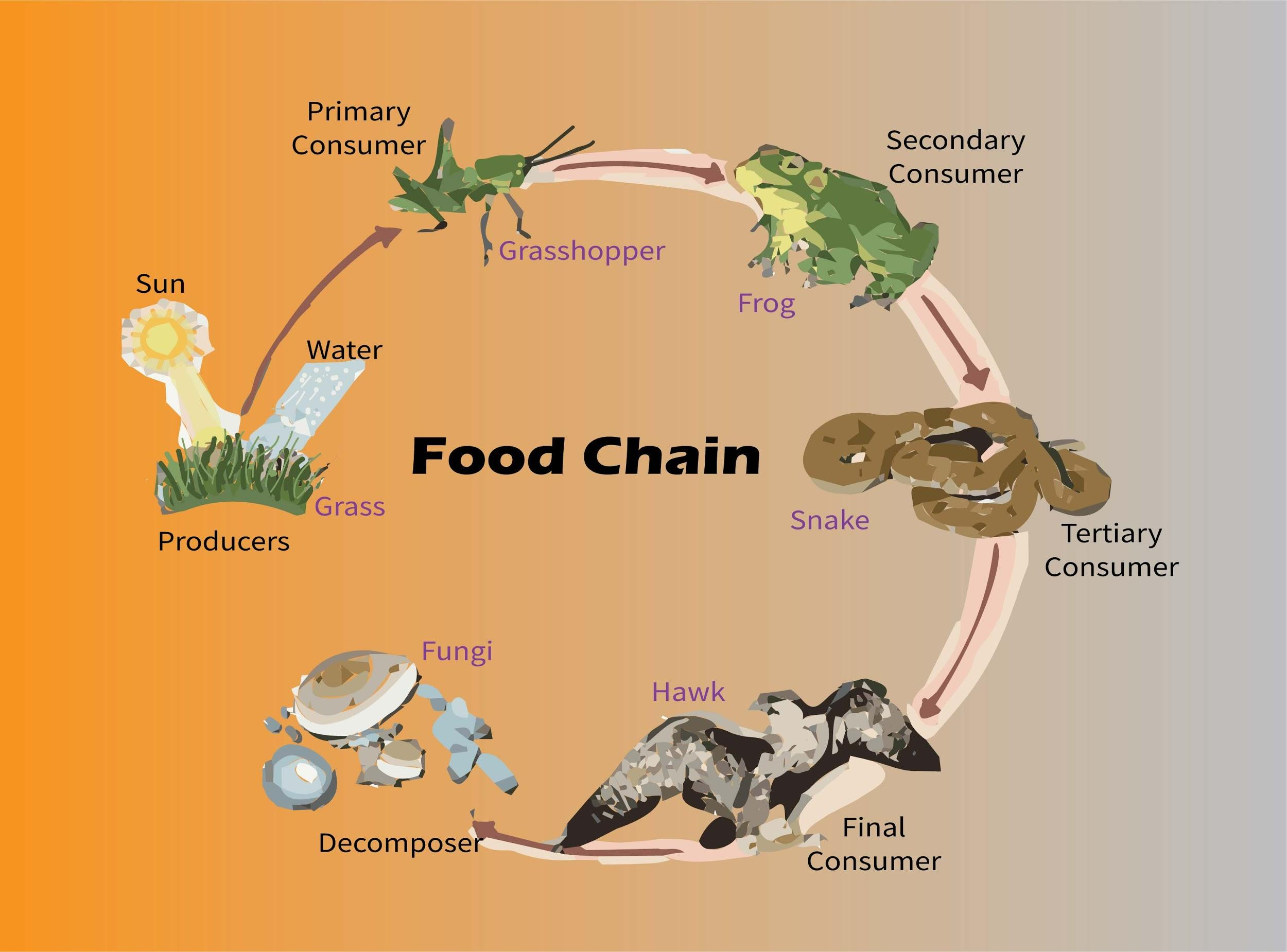
The grasslands ecosystem teems with lifestyles, and at its basis lie the principle manufacturers, the fairway tapestry that sustains all of the meals chain. Those crops have advanced exceptional variations to thrive within the huge, open grasslands, the place daylight, water, and vitamins are frequently scarce.
Photosynthesis: The Lifestyles-Giving Procedure
Photosynthesis, the method in which crops convert daylight into power, is the motive force at the back of the grasslands ecosystem. Grasses, the dominant plant species in grasslands, possess specialised chloroplasts that successfully seize daylight. This power is then used to transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose, the principle power supply for all residing organisms within the ecosystem.
Grazing Animals: Keeping up the Steadiness, Grasslands meals chain
Grazing animals, similar to bison, wildebeest, and zebras, play a an important position in keeping up the well being of grasslands. By way of selectively grazing on sure plant species, they save you anybody species from dominating the ecosystem. This grazing additionally stimulates plant enlargement, encouraging the manufacturing of recent, nutrient-rich shoots that improve a various array of herbivores and their predators.
Customers within the Grasslands Meals Chain

Customers within the grasslands meals chain play a an important position in keeping up the ecosystem’s steadiness. They devour manufacturers, moving power and vitamins during the meals internet.
Customers will also be classified in keeping with their feeding behavior:
Herbivores
- Herbivores devour best plant subject.
- Examples come with:
- Bison: Graze on grasses and sedges.
- Pronghorn antelope: Feed on quite a lot of plant species, together with grasses, forbs, and shrubs.
Carnivores
- Carnivores devour different animals.
- Examples come with:
- Coyotes: Hunt small rodents, rabbits, and birds.
- Wolves: Predators that focus on huge herbivores like bison and deer.
Omnivores
- Omnivores devour each plant and animal subject.
- Examples come with:
- Bears: Feed on berries, nuts, bugs, and small mammals.
- Raccoons: Scavengers that devour quite a lot of plant and animal fabrics.
Trophic Ranges
Customers can be arranged in keeping with their trophic stage:
| Trophic Stage | Customers |
|---|---|
| Number one Customers | Herbivores |
| Secondary Customers | Carnivores that prey on herbivores |
| Tertiary Customers | Carnivores that prey on different carnivores |
Decomposers within the Grasslands Meals Chain
Decomposers are an important avid gamers within the grasslands ecosystem, liable for breaking down lifeless crops and animals, returning vitamins to the soil, and supporting the expansion of recent lifestyles.
The grasslands host a various neighborhood of decomposers, together with micro organism, fungi, and bugs. Each and every team performs a particular position within the decomposition procedure:
Micro organism
- Micro organism are microscopic organisms that ruin down natural subject into more practical compounds.
- They’re liable for the preliminary decomposition of lifeless plant and animal subject matter.
Fungi
- Fungi are higher organisms that use enzymes to damage down complicated natural subject, similar to cellulose and lignin.
- They play a key position within the decomposition of wooden and different plant fabrics.
Bugs
- Bugs, similar to ants, beetles, and termites, assist ruin down natural subject through chewing it and exposing it to micro organism and fungi.
- Additionally they assist aerate the soil, which improves drainage and nutrient availability.
The decomposition procedure is very important for the total functioning of the grasslands ecosystem. It recycles vitamins, making them to be had to crops, and creates a wholesome soil setting for the expansion of recent crops.
Meals Internet Interactions
The grasslands meals chain is a fancy internet of interconnected relationships between other species. Each and every species performs a particular position within the ecosystem, and adjustments in a single species inhabitants will have ripple results all the way through all of the meals internet.
Predator-Prey Relationships
One of the vital necessary relationships within the grasslands meals chain is the predator-prey courting. Predators, similar to wolves, coyotes, and foxes, depend on prey animals, similar to rabbits, mice, and deer, for meals. The inhabitants of predators is immediately associated with the inhabitants of prey.
When the prey inhabitants is top, the predator inhabitants may also be top. When the prey inhabitants is low, the predator inhabitants may also be low.
Symbiotic Interactions
Along with predator-prey relationships, there also are a variety of symbiotic relationships within the grasslands meals chain. Symbiosis is an in depth courting between two other species that advantages each species. One instance of symbiosis within the grasslands is the connection between grasses and micro organism.
Grasses supply micro organism with a spot to reside, and micro organism assist grasses take in vitamins from the soil.
Affect of Adjustments in One Species Inhabitants
Adjustments in a single species inhabitants will have a ripple impact all the way through all of the meals internet. As an example, if the inhabitants of rabbits decreases, the inhabitants of wolves will even lower. It’s because wolves depend on rabbits for meals. The lower within the wolf inhabitants will then result in an build up within the inhabitants of mice, which might be a prey animal for wolves.
The rise within the mouse inhabitants will then result in a lower within the inhabitants of grasses, which might be a meals supply for mice.
Threats to the Grasslands Meals Chain
The grasslands ecosystem faces a number of threats that may disrupt its refined steadiness and steadiness. Those threats come with habitat loss, overgrazing, and local weather exchange.
Habitat Loss
Habitat loss happens when herbal grasslands are transformed to different makes use of, similar to agriculture, city building, or mining. This lack of habitat reduces the volume of meals and safe haven to be had to grassland organisms, resulting in inhabitants declines and attainable extinction.
Overgrazing
Overgrazing happens when farm animals are allowed to graze in grasslands at densities that exceed the wearing capability of the land. This can result in the degradation of crops, soil erosion, and a discount in biodiversity. Overgrazing too can disrupt the meals chain through decreasing the supply of crops for number one customers, similar to herbivores.
Local weather Alternate
Local weather exchange is changing the temperature and precipitation patterns in grasslands around the globe. Those adjustments can have an effect on the expansion and distribution of plant species, resulting in shifts within the composition of the grassland ecosystem. Local weather exchange too can build up the frequency and severity of droughts and wildfires, which will additional injury grassland habitats.
Professional Solutions
What’s the number one supply of power within the grasslands meals chain?
The principle supply of power within the grasslands meals chain is the solar. Vegetation, the manufacturers within the ecosystem, use daylight via photosynthesis to transform carbon dioxide and water into glucose, which serves as the basis of the meals chain.
What are the key threats to the grasslands meals chain?
The grasslands meals chain faces a number of threats, together with habitat loss because of urbanization and agriculture, overgrazing through farm animals, and local weather exchange. Those threats can disrupt the subtle steadiness of the ecosystem, resulting in species loss and ecosystem degradation.

